 如果您点击这里,此页面将被翻译成中文。
如果您点击这里,此页面将被翻译成中文。
 如果您点击这里,此页面将被翻译成中文。
如果您点击这里,此页面将被翻译成中文。
 如果您点击这里,此页面将被翻译成中文。
如果您点击这里,此页面将被翻译成中文。
 如果您点击这里,此页面将被翻译成中文。
如果您点击这里,此页面将被翻译成中文。
International and Public Schools In Malta,Organisation of the education system and of its structure
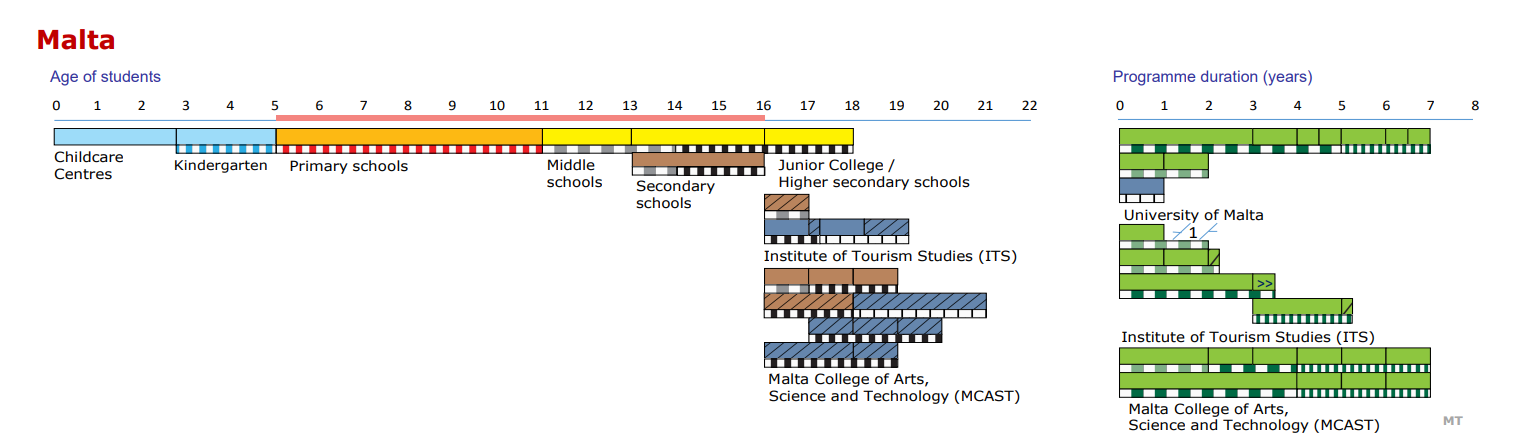
Malta’s educational system is divided into four stages: pre-primary (ages 3–5), primary (ages 5–11), secondary (ages 11–16) and tertiary. Pre-primary education is optional but fully funded by the state.
International Schools
Malta is home to several international schools that cater to expatriate families and offer curricula from various countries. Here’s a list of notable international schools in Malta.
St. Edward’s College
-Location: Cottonera, Cospicua
-Curriculum: Offers the British curriculum (IGCSEs and A-Levels) alongside the International Baccalaureate (IB) Diploma Programme.
-Languages: English and Maltese

Chiswick House School & St. Martin’s College
Location: San Gwann and Naxxar
Curriculum: Offers the British curriculum, including IGCSEs and A-Levels, as well as the International Baccalaureate (IB) Diploma Programme.
Languages: English

San Andrea School
Location: Pembroke
Curriculum: British curriculum, offering IGCSEs and A-Levels.
Languages: English



Public Schools











The University of Malta
The University of Malta, established in 1592, is the highest institution of learning in Malta and one of the oldest universities in Europe. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the University of Malta.
History and Overview
- Founded: 1592
- Location: Msida, Malta
- Type: Public university
Academic Structure
- Faculties: The university is organized into multiple faculties and institutes, including:
- Faculty of Arts
- Faculty of Education
- Faculty of Engineering
- Faculty of Health Sciences
- Faculty of Law
- Faculty of Science
- Faculty of Social Wellbeing
- Faculty of Theology
- Institute of Earth Systems
- Institute of Space Sciences and Astronomy
- Programs: Offers a wide range of undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral programs across various fields, including humanities, science, engineering, medicine, and social sciences.
Research and Innovation
- The University of Malta is involved in various research initiatives and projects, often collaborating with international institutions.
- It has research centers focused on areas like digital sciences, sustainable energy, and marine sciences.
Campus and Facilities
- Main Campus: Located in Msida, it includes modern facilities such as libraries, laboratories, and lecture halls.
- Additional Campuses: There are also specialized facilities, such as the Medical School in Mater Dei Hospital and the Institute of Earth Systems in Marsaxlokk.
International Collaboration
- The University of Malta has partnerships with numerous universities and institutions worldwide, fostering student and staff exchange programs and collaborative research.
Student Life
- Student Organizations: There are various student clubs, societies, and organizations catering to diverse interests, including academic, cultural, and recreational activities.
- Accommodation: Provides options for student housing and has support services to assist with living arrangements.
Language and Culture
- Languages: Courses are primarily taught in English, but there are also programs available in Maltese and other languages.
- Cultural Integration: The university integrates Maltese cultural and historical perspectives into its curricula, enhancing the educational experience.
Notable Alumni
- The University of Malta has produced several notable alumni who have made significant contributions in fields like politics, science, and the arts.
Community and Impact
- The university plays a crucial role in Malta’s educational system, contributing to the country’s academic, professional, and cultural development.
- Faculties: The university is organized into multiple faculties and institutes, including:









